The US went through a major financial crisis in 2008 when state banks all started filing for bankruptcy and people’s hard-earned money all went to vain, the shortcomings of our economic system were brought about.
Our economic system is centralized; it has a central authority, the government. It can raise and reduce the value of money as and when required.
After people lost a lot of money and faith in the 2008 financial crisis in the US, they started wishing for a system of money that would overcome this shortcoming; having a central authoritative figure. This new system should allow for people to be in charge of their own money and spend it without involving a third-party system like a bank.
The Birth of Bitcoin

Around the same time, a mysterious developer/s who went with the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto appeared out of nowhere with a whitepaper for Bitcoin introducing it as a ‘purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution’.
Nakamoto introduced a system for electronic transactions ‘without relying on trust’. This piqued people’s interests especially after having lost all beliefs in banks and governmental systems to secure their money.
Bitcoin solved this problem by ensuring a system where governmental intervention by changing the value of the currency would have no effect on the value of bitcoins. This way, the value of bitcoins only depended on the supply and demand of bitcoins in the market.
It also fixed the number of bitcoins that could ever be in circulation and the rate at which bitcoins could be produced and bought. The maximum number of bitcoins cannot go beyond the limit (21 million BTC) because of the code used in the designing of Bitcoin. This code is visible to everyone on the network so people can check for themselves.
The creation of bitcoin was one of the most significant financial waves of the 21st century. And this was all made possible by its underlying technology known as ‘Blockchain’.
What Is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that stores data such that it can be accessed by everyone and modified only when a certain consensus is reached.
The term ‘blockchain’ was coined by Stuart Haber and W Scott Scornetta in 1991 as a cryptographically secured chain of blocks.
How Does A Blockchain Work?
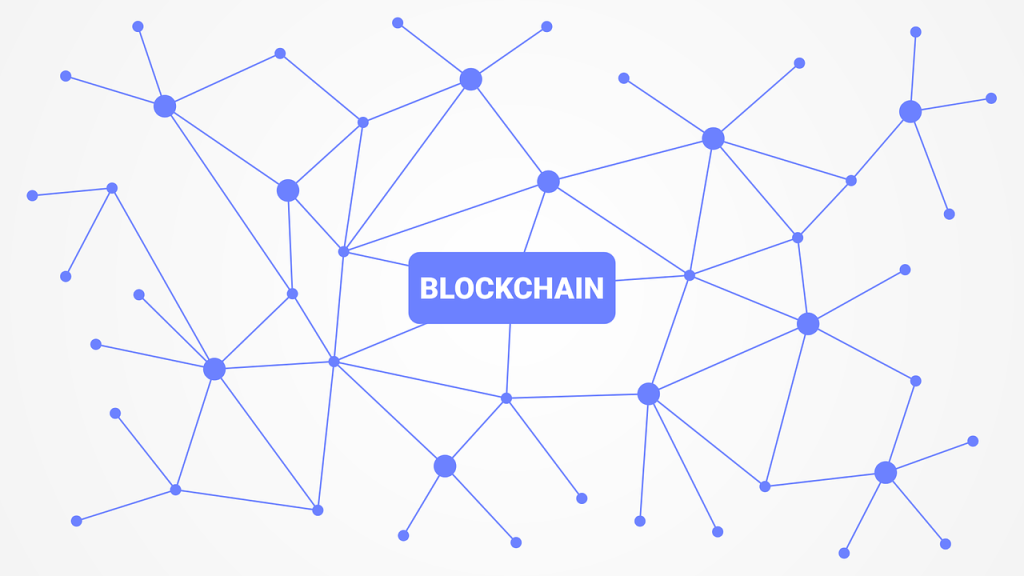
A blockchain stores data or information together in chunks known as ‘blocks’ and these blocks are then chained together to form a chain; hence the name blockchain.
Blocks have a certain limit or capacity to how much data can be stored in them. When new data comes, a new block is created and data is stored in it. Once the block is filled, it is chained with the previous block. All the data that follow the ones in the last block are then added to a newly formed block, which is also chained to the previous block once it’s full.
Each block is given a certain hash and timestamp of when it was added to the chain. When blocks are filled, the data in it is irreversible and cannot be modified unless people on the network reach a majority agreement to do so. All the users/computers known as ‘nodes’ in the blockchain together handle and approve of any transactions and changes. Since each node has its own copy of the data in the blockchain, it is easier to cross-check references when someone maliciously tries to tamper with the data in the node.
Why Blockchain and How is it different from traditional ledgers?
- It is decentralized
Decentralization in blockchain refers to transferring the control of decision making and control to people on the network instead of a third-party individual or organization. Decentralized networks don’t require people to trust each other, as everyone on the network is in equal power and authority to control transactions on the network. There is no single point of failure or vulnerability.
Since data in a blockchain is immutable, only when the majority of the nodes agree to modify anything changes can be made. There are various ways to regulate consensus in a blockchain; proof of work, proof of stake, proof of time elapsed, proof of authority, and many many more. Each blockchain will adapt to a suitable method of consensus for decision-making.
- It solves the double-spending problem
With regards to digital money, the double-spending problem means forging digital money and using it for two different trades. With traditional financial systems, trusted third-party systems like banks and payment gateways are issued. And the government is responsible for keeping them honest and trustworthy.
Since blocks in a blockchain are time-stamped and strictly chronological, when the same bitcoin is being used in two different transactions, we can tell by the timeline which of the two transactions is valid. This removes the need for third-party systems to validate a transaction.
Before confirmation, all transactions are kept in the ‘mempool’, a list of pending transactions. Only when it is confirmed by nodes, it can be added to the blockchain.
- All transactions are secured by node runners and cryptography
Node runners verify all transactions and secure the blockchain. Besides that, each block in a blockchain is secured by cryptographic keys (a string of data) called a hash. Blocks contain a hash of their own and the hash of the previous blocks. When someone tries to tamper with data in one block, the hash of the block changes and no longer corresponds with the hash in its preceding block. This invalidates the rest of the chain.
To successfully tamper with data, you would have to tamper data in all the blocks in the blockchain across all copies in the network; which is next to impossible. So, there is not a single point of failure in a blockchain.

- Faster transactions
Live node runners across the network verify all transactions through consensus mechanisms. And because of peer-to-peer sharing, you can directly send data to another node without the interference of a third party. All of this leads to faster transactions.
Blockchains gained popularity with cryptocurrencies in the market. Bitcoin is only the first real implementation of Blockchain. But, the potential of this trustless digital ledger system goes beyond digital currencies.
Blockchains can be used as a transparent and secure way to reduce voter fraud, ensuring voters’ privacy and effectively reducing the cost of the election. It can also allow secure online voting.
It can be adapted to keep government records, medical records in hospitals to land registration records in real estate. With blockchains, NFTs (Non-fungible tokens) can also be stored with enhanced security. All in all, blockchain technology can truly revolutionize the world.