Overview:
3D printing is the process of making a physical object from a three-dimensional digital model. It is a part of additive manufacturing technology where the desired product is created by laying successive superfine layers of material. 3D printing uses computer-aided design (CAD) software or 3D object scanners to make a digital prototype of the final product. Then the data is directed to a printer that deposits the required material, layer by layer, in precise geometric shapes.
3D printing has been found to be incredibly cost-effective and time-effective in manufacturing any object. It is already being used to build small, delicate parts in machines, aircraft, and cars, as well as to build big structures like a house. Experts refer to 3D printing as the tool for the modern industrial renaissance.
To truly understand what improvement 3D printing brings in manufacturing, we have to understand how anything is manufactured. There are many methods that one can adopt to create an object. Here are some main and the most popular ones.
- Subtractive method: In this method, a big material is broken, cut, milled, or carved into the desired structure. One example of manufacturing using the subtractive method is sculpting a statue. A big stone, marble, wood, or any other desired material is sculpted into the final product.
- Molding: Another way to create an object is to take a substance in solid form, melt it, and pour it into a shape-forming mold/cast to give it the shape you like. Chocolates and soaps are made using the molding technique.
- Forming: Here you have a block of material and you apply force or heat to it to change its structure to whatever you desire.
- Additive method: This method is the basis of 3d printing. Here you have nothing, to begin with, and you add material layer by layer to create a shape that you want. It has been around for a very long time. Today it is rebadged with a new name, 3d printing.
More accurately, 3d printing is a part of additive manufacturing. It allows designers to manufacture an object at a fraction of the cost and time of standard means like forming, casting, and sculpting. It creates less material wastage than these traditional methods.
How 3D printing works:
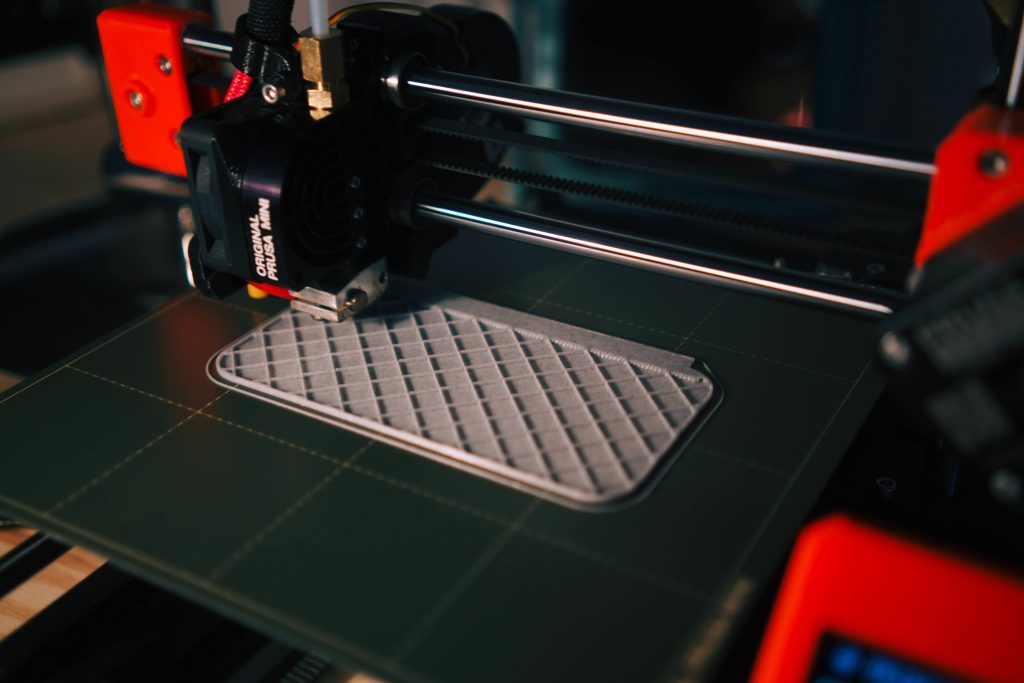

There are many different types of 3D printing processes like Vat Polymerization, Material Extrusion, Material Jetting, Binder Jetting, etc. But nearly all of them consist of these basic steps:
- Prototyping
Prototyping is the process of creating a working model of the final product. It is the simulation of the final product, how it looks and feels, and its features. Before anyone can print an object with a 3D printer, they need to design the model using computer software. They can make their own unique designs through CAD software or visit websites like Shapeways or Thingiverse to find objects other users have 3D modelled. The object model is saved in a stereolithography (STL) or an additive manufacturing file (AMF) format.
During the modelling step, any defects or possible risks of the final product can be identified. Most CAD software can also help in identifying design errors that could impact the final structure.
- Printing
After the prototype is built and checked for errors, you can send it to a printer. The printer will use the instructions in the file to decide where and how the building material needs to be deposited.
3D printers may use different materials to build an object, but the most commonly used material is thermoplastic. Printers will have thermoplastic spools in the back of the device. When it is ready to print, it will pull the material through a tube, melt it, and deposit it onto the plate, where it instantly cools. It lays down the bottom layer first and then does the same for layers above it until you have the full object.
- Finishing
The final step is finishing, which suggests making final touches to the printed object. You may need to add some solvent to remove any imperfections and create a smoother surface. If any supports were used to hold the object during printing, you may need to remove that. The printed object then needs to be tested for any faults in design or functionality.
To pick the right process for 3D printing, you need to consider the required properties of the material: strength, hardness, impact strength, etc, the design requirements like smooth surface, strength, heat resistance, as well as the accuracy of the printer, and scale of the build.
Now, why 3D printing?
So what, it can build things? We have been building things since the beginning of civilization without 3D printing technology. Why is now a good time to adopt this technology and why is it better than our traditional manufacturing tools? Here’s why:
- Rapid Prototyping

Companies have been using 3D printers to create prototypes since the late seventies. Using 3D printers to create a prototype is called rapid prototyping. Designers can build designs and any modifications quickly and easily. 3D printing also allows for small batches and in-house production, so there is no dependency on suppliers.
- Rapid Manufacturing
It is so incredibly easy and quick to 3D print an object. There is no cutting, sculpting, or moulding of a material required, you don’t need to wait for large building materials to be delivered and 3D printing also removes the need for human labour.
Recently, China 3D printed 10 houses in a single day with a cost of $5000 per house. This only proves how cost and time-efficient 3D printing can be in large-scale manufacturing too.
- Customization
The design is based on computer-aided designs CAD, so there is no change in the cost of production when any alterations are made in the design. Numerous objects can be printed at the same time according to one’s unique, individual requirements. This kind of mass customization also puts 3D printing leaps ahead of traditional manufacturing.
- Easy
3D printing eliminates the need for large tools and machines. This decreases the cost, labour work, and time of product manufacturing significantly.
- Closes the gap between manufacturing and consumption
In disaster-struck areas, where relief and construction materials are urgently needed, waiting for a supplier to transport them is very inefficient. In the same way, another case where transportation for essentials is very large scale and not always feasible is transporting things to space. With 3D printers, one can print things when and as required. There are many such cases where 3D printing has proved beneficial.
- Sustainable and environment-friendly
Like we already discussed, 3D printing uses only the amount of material as the actual product requires, so it is a sustainable way to build things. There is no wastage of material. 3D printing also leaves less carbon footprint than traditional methods of manufacturing.
Applications of 3D printing:
Let’s look at what fields 3D printing is most popularly used.
- Medical field
The medical field is one of the earliest adopters of 3D printing technology. There is also the largest potential in this field because of the customization and efficiency of 3D printing. It is utilized in the following ways:
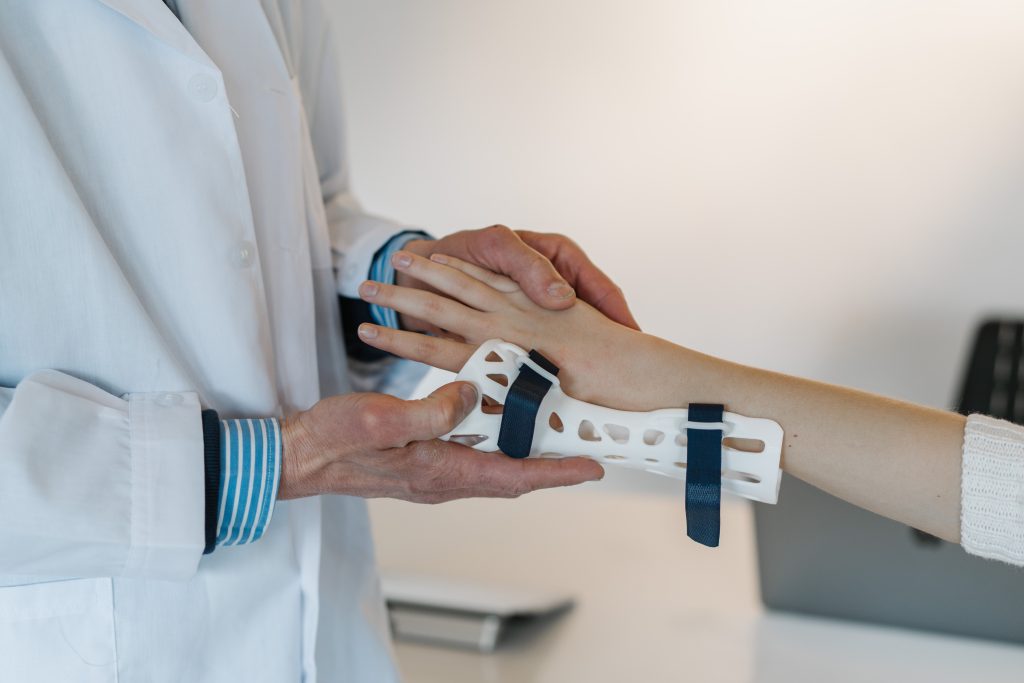
- Making metal casting for dental crowns
- Making dental aligners
- Hip and knee implants
- Hearing aids, orthotic insoles for shoes, personalized prosthetics
- 3D printing of skin, bone, tissues
- Using human cells and tissues to print organs
- Aerospace
The aerospace sector is also one of the earliest adopters of 3D printing technology. Some high-profile brands that use 3D printing include Boeing, GE Aviation, Airbus, and NASA. Due to the weight and cost reductions, 3D printing is used in building Jigs and fixtures, engine compartments, air ducts, panels, lights, dashboard components, etc.
- Automotive
Many automotive companies use 3D printing technologies to build efficient prototypes and print lightweight parts. It also allows for the production of new and bespoke parts for testing or small-scale manufacture. Spare parts can be printed overnight and are ready for testing instead of a larger manufacturing run.
Besides these, 3D printing is also rapidly impacting jewellery making, art, sculpture, architecture, fashion, and even the food industry.
The Bottom Line:
To say whether 3D printing will bring another industrial revolution or not is rather too early to decide. Although it has been around for a while, 3D printing has seen slow but sure progress in many fields. It is an exceptional tool for custom parts making and rapid prototyping, but it will take time until 3D printing can be fully commercialized and used in personal manners. It could democratize the manufacturing of goods. And as the technology advances, it could also be used in large-scale construction beyond just testing and experimenting.
Where the high volume of production of simpler parts is required, traditional manufacturing is more feasible. But by lowering the cost of 3D printing, we can introduce it outside of industrial fields and into schools, homes, and offices. Until then, the question remains of how 3D printing could be relevant to people in more common ways.